前言
我们通过官方文档使用SpringMVC,用Tomcat来跑时,需要配置下面这段代码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45package com.lnw.config;
import org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer;
import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRegistration;
import javax.servlet.annotation.HandlesTypes;
/**
* 为什么实现了WebApplicationInitializer就可以被Tomcat所管理?
* 先看一个注解和一个类
* @see HandlesTypes
* @see ServletContainerInitializer
* 这两个一般成对出现的
* 在Tomcat启动的时候,会自动去寻找所有实现该接口的类
* 找到这个类后,里面唯一的实现方法需要一个Set参数
* 这些参数Tomcat会帮你去找,参数的类型是@HandlesTypes里面的value值
* Spring在org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer中引用该注解并实现ServletContainerInitializer
* value值就是WebApplicationInitializer
* @see SpringServletContainerInitializer
*/
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("----init my ServletContext----");
// Load Spring web application configuration
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ac.register(AppConfig.class);
// ac.refresh();
// Create and register the DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet servlet = new DispatcherServlet(ac);
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet("app", servlet);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/*");
}
}
AppConfig.class1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11package com.lnw.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.lnw")
@EnableWebMvc
public class AppConfig {
}
这样,当我们整合Tomcat来跑时(一般都是Tomcat插件),就会执行onStartup方法来启动SpringMVC
源码解析
我们看下我们实现的接口WebApplicationInitializr1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16package org.springframework.web;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
public interface WebApplicationInitializer {
/**
* Configure the given {@link ServletContext} with any servlets, filters, listeners
* context-params and attributes necessary for initializing this web application. See
* examples {@linkplain WebApplicationInitializer above}.
* @param servletContext the {@code ServletContext} to initialize
* @throws ServletException if any call against the given {@code ServletContext}
* throws a {@code ServletException}
*/
void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException;
}
发现它还是Spring的东西,如果要随着Tomcat启动执行的话,那也得是Servlet或者Tomcat里面的东西吧
在Tomcat启动的时候,它会去扫描classpath下的services文件夹(包括依赖的项目),如果文件名是javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer,就把文件里面的值读取出来(值是个类,读取出来后加载)
SpringMVC的web项目下就有一个services文件夹,而且文件名也是那个,里面的值是SpringServletContainerInitializer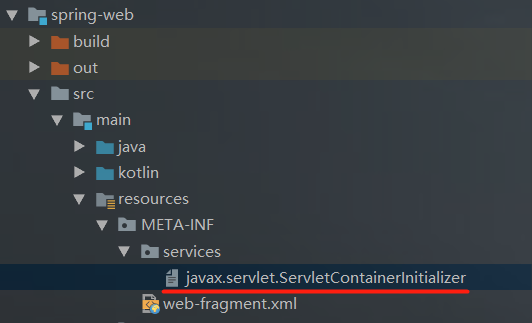

我们查看SpringMVC里面的类SpringServletContainerInitializer1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53package org.springframework.web;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ServiceLoader;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.HandlesTypes;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<>();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}
注解@HandlerTypes里面的value值正是我们上面的那个WebApplicationInitializer
下面我们先来说下Tomcat里面的原理
Tomcat
就只说关键部分
Tomcat在启动的时候,会配置Context,配置Context需要ContextConfig
ContextConfig的核心就是webConfig 方法,下面主要看几条主要的代码
org.apache.catalina.startup.ContextConfig#webConfig1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55org.apache.catalina.startup.ContextConfig#webConfig
// Step 1. 读取各个jar模块和fragments
Map<String,WebXml> fragments = processJarsForWebFragments(webXml, webXmlParser);
// Step 2. 排序fragments
Set<WebXml> orderedFragments = null;
orderedFragments =
WebXml.orderWebFragments(webXml, fragments, sContext);
// Step 3. 寻找所有的ServletContainerInitializer实现
// SpringMVC也是基于这个过程开展的
if (ok) {
processServletContainerInitializers();
}
// Step 4. 处理/WEB-INF/classes文件夹下面的注解了@HandlesTypes
// 这一步很重要
Map<String,JavaClassCacheEntry> javaClassCache = new HashMap<>();
if (ok) {
WebResource[] webResources =
context.getResources().listResources("/WEB-INF/classes");
// Step 5. 处理所有的jar中有关的@HandlesTypes
if (ok) {
processAnnotations(
orderedFragments, webXml.isMetadataComplete(), javaClassCache);
}
// Step 6. 将所有的fragments.xml合并
if (ok) {
ok = webXml.merge(orderedFragments);
}
// Step 7a,将所有的web.xml合并
// merge tomcat-web.xml
webXml.merge(tomcatWebXml);
。。。
// Step 11. 将扫描到的所有实现了ServletContainerInitializer类添加到StandardContext容器中
if (ok) {
for (Map.Entry<ServletContainerInitializer,
Set<Class<?>>> entry :
initializerClassMap.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().isEmpty()) {
context.addServletContainerInitializer(
entry.getKey(), null);
} else {
context.addServletContainerInitializer(
entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
}
通过注释大概可以知道每段代码的作用
其中这段代码很重要 processServletContainerInitializers();
还有就是最后的Step 11将扫描到的类添加到Context 中
也就是说,Tomcat启动的时候,会使用ClassLoader扫描classes路径下所有的类,找出实现了ServletContainerInitializer类并保存,然后在随后的启动中调用ServletContainerInitializer
的onStart方法1
void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> c, ServletContext ctx) throws ServletException;
集合Set是存放注解@HandlesTypes中的类,目的是在特定的ServletContainerInitializer中启动的时候做另外的操作
SpringMVC跟Tomcat
上面我们讲到Tomcat启动的时候会扫描到所有实现了ServletContainerInitializer的类,而我们的SpringServletContainerInitialzer就是SpringMVC跟Tomcat的桥接
我们再来看下SpringServletContainerInitializer的源码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53package org.springframework.web;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ServiceLoader;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.HandlesTypes;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<>();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}
因为SpringServletContainerInitializer实现了ServletContainerInitializer,所以会被Tomcat扫描存储到Context,并且因为该类上面注解了@HandlesTypes,里面的value为WebApplicationInitializer.class,所以Tomcat会将实现了WebApplicationInitializer的类扫描出来封装到Set中。
Tomcat的启动中,会调用所有的ServletContainerInitializer的onStartup方法来初始化并启动StrandContext容器,所以SpringServletContainerInitiar的onStartup方法就会被调用
在org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer#onStartup方法中,通过一个for循环启动所有的WebApplicationInitializer1
2
3for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
就是这样,执行了SpringMVC官方文档的这段代码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("----init my ServletContext----");
// Load Spring web application configuration
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ac.register(AppConfig.class);
// ac.refresh();
// Create and register the DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet servlet = new DispatcherServlet(ac);
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet("app", servlet);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/*");
}
}